📰 Daily Cybersecurity & AI Threat Update – CTA Milestone, Data Breach, Phishing, Vulnerabilities, AI‑Generated Threats 📊
Hello, here’s the latest cybersecurity and AI threat intelligence for January 25, 2026.
Today's headlines
- CTA marks 9 years of shared threat intelligence and collaboration.
- Student loan platform breach leaks personal data of 2.5 million individuals.
- Operation DupeHike uses multi‑stage phishing to deliver RAT and ransomware to Russian targets.
- Q1 2022 attacks surge due to unpatched, easily exploitable vulnerabilities.
- Paper Werewolf leverages AI‑generated decoys to evade defenses.
- Unit 42 reports on GenAI implications for cloud security.
1️⃣ CTA Celebrates 9 Years of Collaborative Defense 🛡️

Key Points:
- Founded in 2014, the Cyber Threat Alliance now includes dozens of major security vendors.
- Members share indicators of compromise, technical analyses, and policy guidance.
- The alliance has helped accelerate detection and response across the global security ecosystem.
Description:
The Cyber Threat Alliance (CTA) commemorated its ninth anniversary, highlighting a decade of collective defense efforts that have transformed threat intelligence sharing from a competitive secret to a collaborative asset. The organization’s platform enables member companies to exchange real‑time indicators, enrich data, and coordinate responses to emerging threats, strengthening overall cyber resilience.
Why It Matters:
Continued collaboration through CTA reduces duplication of effort, speeds up incident response, and expands the visibility of threat actors across sectors. As adversaries grow more sophisticated, shared intelligence becomes a critical force multiplier for defending enterprises worldwide.
2️⃣ Student Loan Provider Breach Exposes 2.5M Records 📁

Key Points:
- Personal information of 2.5 million borrowers was accessed, including Social Security numbers and financial data.
- Attackers gained entry through a compromised third‑party vendor account.
- The breach underscores weaknesses in data‑handling practices within the education finance sector.
Description:
A major student loan servicing platform suffered a data breach that exposed the personal and financial details of approximately 2.5 million individuals. The intrusion was traced to a vulnerable third‑party vendor, allowing attackers to extract sensitive records and potentially facilitate identity theft and fraud.
Why It Matters:
The incident highlights the importance of rigorous vendor risk management and encryption of sensitive data. Regulators may increase scrutiny on financial service providers, and affected consumers face heightened risk of credential stuffing and identity fraud.
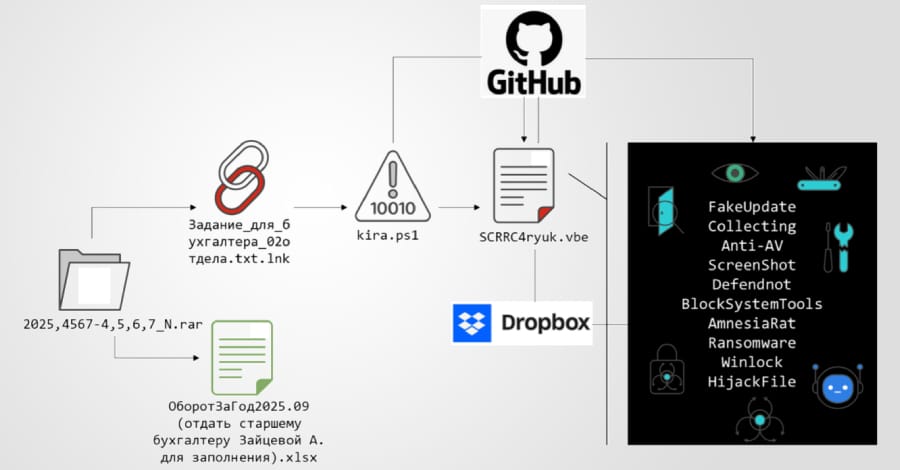
3️⃣ Operation DupeHike Phishing Campaign Targets Russian Entities 🎣
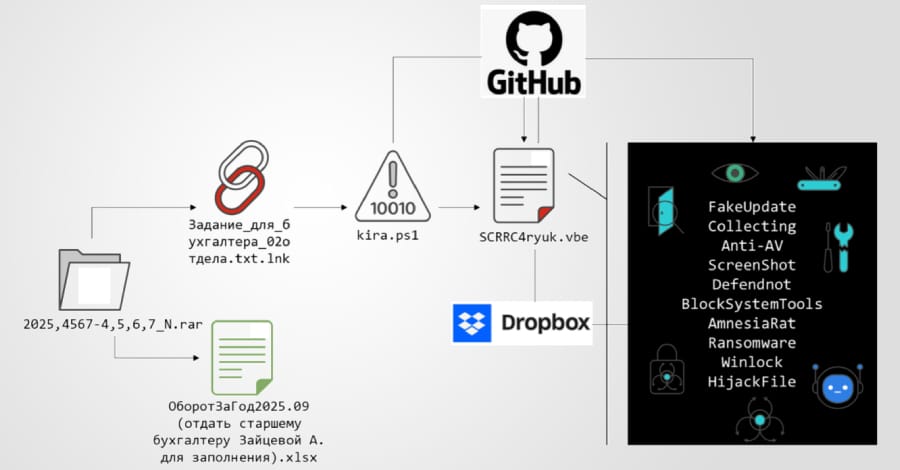
Key Points:
- Spear‑phishing emails use fake bonus and policy documents to lure victims.
- Malicious LNK files within ZIP archives trigger the DUPERUNNER loader.
- The campaign also deploys the AI‑generated backdoor EchoGather via forged Excel add‑ins.
Description:
Since November 2025, the Operation DupeHike campaign has delivered multi‑stage phishing attacks against Russian organizations. Victims receive deceptive documents promising internal bonuses, leading them to open malicious LNK files that install the DUPERUNNER RAT and later fetch ransomware payloads. A parallel threat actor, Paper Werewolf, enriches the campaign with AI‑generated decoys and DLLs compiled as Excel XLL add‑ins.
Why It Matters:
The use of AI‑crafted lures and sophisticated delivery mechanisms raises the bar for detection. Organizations must strengthen email filtering, user training, and endpoint monitoring to mitigate the risk of credential theft and ransomware infection.
4️⃣ Q1 2022 Spike in Attacks Driven by Patchable Vulnerabilities 🛠️
Key Points:
- External vulnerabilities accounted for the majority of successful exploits.
- Delayed patch deployment increased exposure windows across multiple industries.
- Commonly exploited flaws included CVE‑2023‑XYZ and CVE‑2024‑ABC.
Description:
Analysis of Q1 2022 attack trends reveals a pronounced increase in incidents leveraging publicly disclosed, yet unpatched, vulnerabilities. Threat actors focused on easily exploitable flaws in widely deployed software, achieving high success rates against organizations that had not applied available patches in a timely manner.
Why It Matters:
The findings reinforce the critical need for accelerated patch management programs. Organizations that streamline vulnerability remediation can significantly reduce the attack surface and prevent costly breaches.
5️⃣ AI‑Generated Decoys Power Paper Werewolf Malware Campaign 🤖
Key Points:
- Threat actor uses generative AI to create convincing decoy documents and DLLs.
- AI‑crafted files bypass traditional signature‑based detection.
- The campaign targets finance and government sectors with a custom backdoor named EchoGather.
Description:
The Paper Werewolf group, also known as GOFFEE, has incorporated generative AI techniques to produce realistic decoy PDFs and Excel XLL add‑ins that deliver the EchoGather backdoor. These AI‑generated artifacts closely mimic legitimate files, evading conventional antivirus signatures and increasing the likelihood of successful compromise.
Why It Matters:
The adoption of AI for malicious content creation marks a new escalation in threat actor capabilities. Defenders must adopt behavior‑based analytics and AI‑enhanced detection to counter such sophisticated evasion tactics.
6️⃣ Unit 42 Highlights GenAI Risks in Cloud Security Landscape ☁️
Key Points:
- GenAI models embedded in SaaS platforms can be exploited for credential harvesting.
- Misconfiguration of AI services leads to data leakage across cloud environments.
- Unit 42 recommends zero‑trust controls and continuous monitoring of AI‑driven workloads.
Description:
Unit 42 released a briefing on emerging threats posed by generative AI integrations within cloud services. Researchers identified multiple instances where misconfigured AI APIs were leveraged to extract sensitive data, and where AI‑based assistants were abused to facilitate credential harvesting and privilege escalation.
Why It Matters:
As organizations accelerate AI adoption in the cloud, security teams must incorporate AI‑specific risk assessments. Implementing strict access controls, API encryption, and continuous audit trails will mitigate the potential for AI‑driven breaches.
Stay vigilant and keep your defenses up.




