🛡️ Cloudflare patches critical ACME validation flaw, AI‑phishing campaigns spike in Q4 2025. 📊 Privacy watchdogs highlight ICE’s use of Palantir on Medicaid data.

Good morning, here is your daily cybersecurity & AI threat briefing for Jan 25, 2026.
Today's headlines
- Cloudflare resolves ACME path validation bug affecting WAF features.
- AI‑generated phishing emails increased 42% in Q4 2025.
- ICE adopts Palantir analytics on Medicaid datasets, raising privacy concerns.
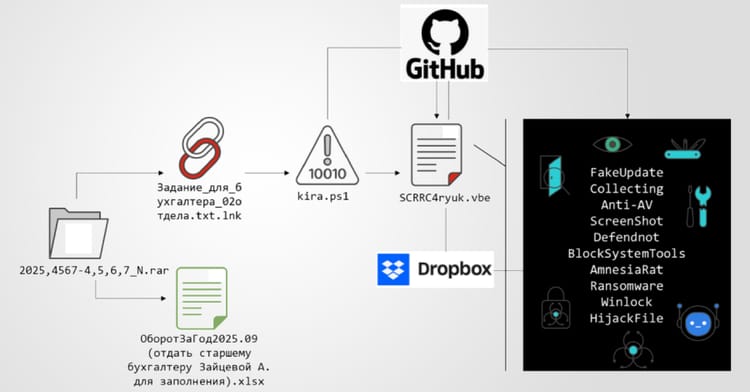
- React2Shell RCE vulnerability seen in scans targeting critical infrastructure.
- BGP route leak detected in Venezuela on Jan 2, 2026.
- Axon’s Draft One AI tool automates police report writing, prompting policy debate.
1️⃣ Cloudflare patches ACME validation vulnerability

Key Points:
- Bug reported by FearsOff on Oct 13, 2025.
- Affected /.well-known/acme-challenge/ path could bypass WAF rules.
- Patch deployed within two weeks, restoring full WAF protection.
Description:
Cloudflare disclosed and mitigated a flaw in its ACME validation logic that allowed certain requests to bypass Web Application Firewall checks. The issue was responsibly reported through the bug bounty program and fixed promptly, with a public advisory released on Jan 19, 2026.
Why It Matters:
The vulnerability could have been leveraged to hide malicious traffic from security controls, potentially exposing millions of websites to attack. Rapid remediation demonstrates effective coordination between researchers and Cloudflare, reinforcing trust in the platform.
2️⃣ AI‑phishing campaigns surge in Q4 2025
Key Points:
- Phishing emails generated by large‑language models grew 42% QoQ.
- Successful credential theft increased 18% compared to 2024.
- Defenders report higher bypass rates of spam filters.
Description:
Security firms observed a sharp rise in AI‑generated phishing emails during the last quarter of 2025. Using advanced language models, attackers produced more convincing narratives and personalized content, leading to a notable uptick in successful credential harvesting.
Why It Matters:
The trend signals that threat actors are adopting generative AI at scale, raising the bar for detection and response. Organizations must update their email security solutions and user training to recognize AI‑crafted social engineering.
3️⃣ ICE uses Palantir on Medicaid data
Key Points:
- Internal report shows Palantir platform ingests Medicaid records.
- Data is used for immigration enforcement analytics.
- Civil liberties groups raise concerns about consent and profiling.
Description:
The Electronic Frontier Foundation released a report detailing how Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) deployed Palantir software to analyze Medicaid data. The tool aggregates health information to support enforcement decisions, prompting criticism over privacy and due process.
Why It Matters:
Linking health data with immigration enforcement creates risks of misuse and discrimination, potentially chilling access to medical care for vulnerable populations. The revelation may influence policy discussions on data sharing restrictions and oversight.
4️⃣ React2Shell RCE hits critical infrastructure
Key Points:
- New remote code execution flaw discovered in React2Shell library.
- Threat actors integrated exploit into scanning tools targeting nuclear facilities.
- Mitigations include patching and network segmentation.
Description:
Researchers identified a remote code execution vulnerability in the popular React2Shell component, allowing attackers to execute arbitrary commands on affected servers. Early exploitation attempts were observed against systems handling nuclear fuel and rare earth element data.
Why It Matters:
The exploitation of a widely used library in critical sectors underscores the need for continuous component monitoring and rapid patch deployment. Failure to address the flaw could lead to severe operational disruptions and data compromise.
5️⃣ BGP route leak in Venezuela observed Jan 2
Key Points:
- Unexpected prefix announcements caused traffic diversion.
- Leak traced to misconfigured router at a regional ISP.
- Mitigation involved coordinated prefix withdrawal.
Description:
On January 2, 2026, a BGP route leak originating from Venezuela resulted in abnormal traffic paths affecting regional internet connectivity. Cloudflare’s Radar team analyzed the incident, revealing a misconfiguration that temporarily exposed traffic to unintended networks.
Why It Matters:
BGP leaks can be leveraged for traffic interception, espionage, or denial‑of‑service attacks. Rapid detection and collaboration among operators are essential to restore routing integrity and prevent potential data exposure.
6️⃣ Axon’s Draft One AI automates police reports
Key Points:
- Generative AI writes initial drafts of incident reports.
- Pilot program deployed in three US police departments.
- Civil liberty groups call for transparency and oversight.
Description:
Law enforcement technology company Axon introduced Draft One, an AI‑powered tool that assists officers by auto‑generating police report drafts based on voice inputs and sensor data. The system aims to reduce paperwork workload and improve documentation consistency.
Why It Matters:
While increasing efficiency, the use of AI in official reporting raises concerns about bias, accuracy, and accountability. Proper governance frameworks are needed to ensure the technology supports, rather than undermines, public trust in policing.
Stay vigilant and keep your defenses up.